Podiatry
PODIATRY, OR PODIATRIC MEDICINE
Podiatry, or podiatric medicine, is a branch of medicine devoted to the study of, diagnosis, and medical and surgical treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle and lower extremity. The term podiatry came into use in the early 20th century in the United Statesand is now used worldwide, including countries such as the United Kingdom andAustralia.
Podiatry is practiced as a specialty in many countries, while in many English-speaking countries, the older title of chiropodist may be used by some clinicians (not to be confused with chiropractic, which is unrelated). In Australia, the title is podiatrist orpodiatric physician and the specialist is the podiatric surgeon. In many non-English-speaking countries of Europe, the title used may be podologist or podólogo. The level and scope of the practice of podiatry vary among countries.

Podiatric surgery
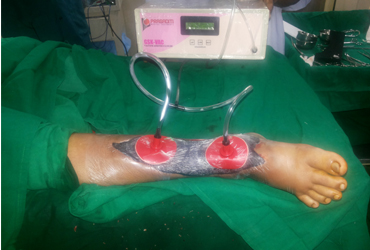
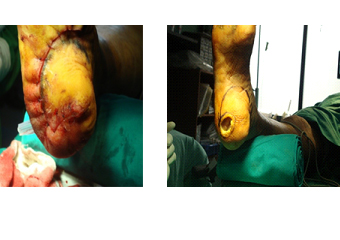
Podiatric surgery is a specialist field in the podiatry profession. Podiatric surgery is the surgical treatment of conditions affecting the foot, ankle and related lower extremity structures by accredited and qualified specialist podiatrists. Podiatric surgery is designed to ensure continued functionality of the foot and ankle areas.
Patients who complain of joint and ligament problems, as well as those with congenital deformities, are offered a plethora of surgical solutions that fix bones, muscles, and joints. Certain podiatric surgeons specialize in minimally invasive surgery, while others perform full reconstructions.
Podiatric sports medicine
Sport podiatry, a sub-specialty of podiatric medicine, involves the expertise in diagnosis of foot and lower limb problems as well as treatments such as joint mobilisation, advanced biomechanical assessments, injection therapy such as corticosteroids, soft-tissue manipulation and trigger point therapy, advanced orthotic therapy, rehabilitation, exercise, strength and conditioning of the lower extremities and footwear prescription for the professional, elite, amateur and young athletes, as well as those who have sustained injuries in day-to-day life.
Sports podiatry covers the following two areas:
Foot and Lower Limb Overuse Injuries
Mechanical performance enhancement to minimise injury and to maximise efficiency
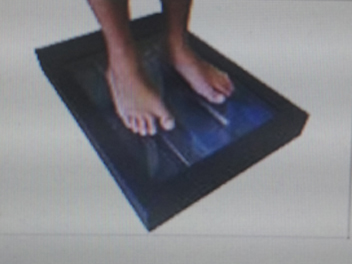
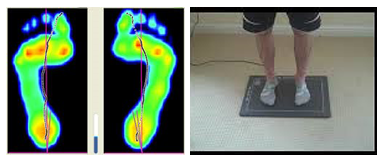
3D Digital Foot Scan
The Scan Any 3D foot scanner is an incredibly accurate instrument. It has replaced the traditional plaster casting method. It uses a dual camera system and specially designed sock to convert the image to a raw 3D file.
The benefit of 3D scanning is reliability of reproducing the image and the ease of storing and sending the information to our orthotic laboratory.
PODIATRY Services Available
Using the best in non-surgical and surgical treatments, our podiatrists treat whatever foot, ankle and leg problems you may have. As a team, our staff also focuses on preventing injuries, and keeping you — and your family — healthy and strong.
We provide care for common foot and ankle issues, such as:
- Tendon strains, tears or ruptures
- Fractures and dislocations
- Sprains and ligament tears
- Bunion deformity
- Hammer toe
- Ankle and lower leg pain
- Heel pain and spurs
- Arthroscopy
- Arthritis
- Flat foot
- Neuroma and nerve problems
- Diabetic foot and ankle-related problems
- Foot and ankle deformities
- Warts on the foot
- Infections, wound problems
- Plantar fasciitis
- Pediatric foot/ankle disorders
- Foot conditions requiring orthotics
- Ingrown toenail, fungal nails
- Foot and ankle conditions that may require surgery